The APG-83 is an active, electronically scanned array (AESA) fire control radar. Building on Northrop Grumman's 40-year legacy producing radars for the F-16, it integrates within the F-16's current structural, power and cooling constraints without Group A aircraft modification. The capabilities of this advanced AESA are derived from the company's family of highly successful 5th generation fighter AESA radars, the F-22's APG-77 and F-35's APG-81.
To counter more sophisticated threats, the world's newest fighter aircraft and legacy fleets are being equipped with AESA radars. The greater bandwidth, speed and agility of AESA radars enable fighter and legacy aircraft to detect, track and identify a greater numbers of targets, faster and at longer ranges in hostile electronic environments. The APG-83 AESA provides capability enhancements over legacy mechanically scanned APG-66 and APG-68 radars to ensure F-16s, F-18s and other 4th generation aircraft remain operationally viable and sustainable for decades to come. Production is underway for global F-16 upgrade and new aircraft production programs.

The F-35 Lightning II is a stealthy, supersonic, multirole fighter designed to meet the requirements of the United States and allied defense forces worldwide for an affordable next generation fighter. It will replace a wide range of aging fighter and strike aircraft currently in the inventories of the U.S. Air Force, Navy, Marine Corps and allied defense forces.
Northrop Grumman is a principal member of the Lockheed Martin-led industry team, which is developing and producing three variants. The F-35A is the conventional takeoff and landing (CTOL) variant, the F-35B is the short takeoff-vertical landing (STOVL) variant, and the F-35C is the carrier variant (CV).
The program's hallmarks — affordability, survivability, sustainability and lethality — are achieved through the use of the most modern military aircraft technologies, state-of-the-art production facilities and a high degree of commonality among the three variants.
Northrop Grumman plays a critical role in the development, demonstration and production of this multirole fighter, including:
- The production of the center fuselage, which forms a significant portion of the aircraft's internal weapons bay and internal fuel capacity.
- The design and production of the AN/APG-81 Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) fire control radar, which brings unmatched capability to air-to-air and air-to-surface missions, complemented by significant electronic warfare and intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance functions.
- The design and production of the AN/AAQ-37 Distributed Aperture System (DAS), which provides simultaneous modes of situational awareness, infrared search and track, missile warning and navigation not available on any other aircraft.
- The design and production of the AN/ASQ-242 Communications, Navigation and Identification (CNI) avionics suite, which can be dynamically programmed to arm the F-35 pilot with multiple-mission capabilities engineered for seamless transition from one mission phase to the next.
- The development of mission systems and mission-planning software.
- The development of pilot and maintenance training system courseware.
- The management of the team's use, support and maintenance of low-observable technologies.
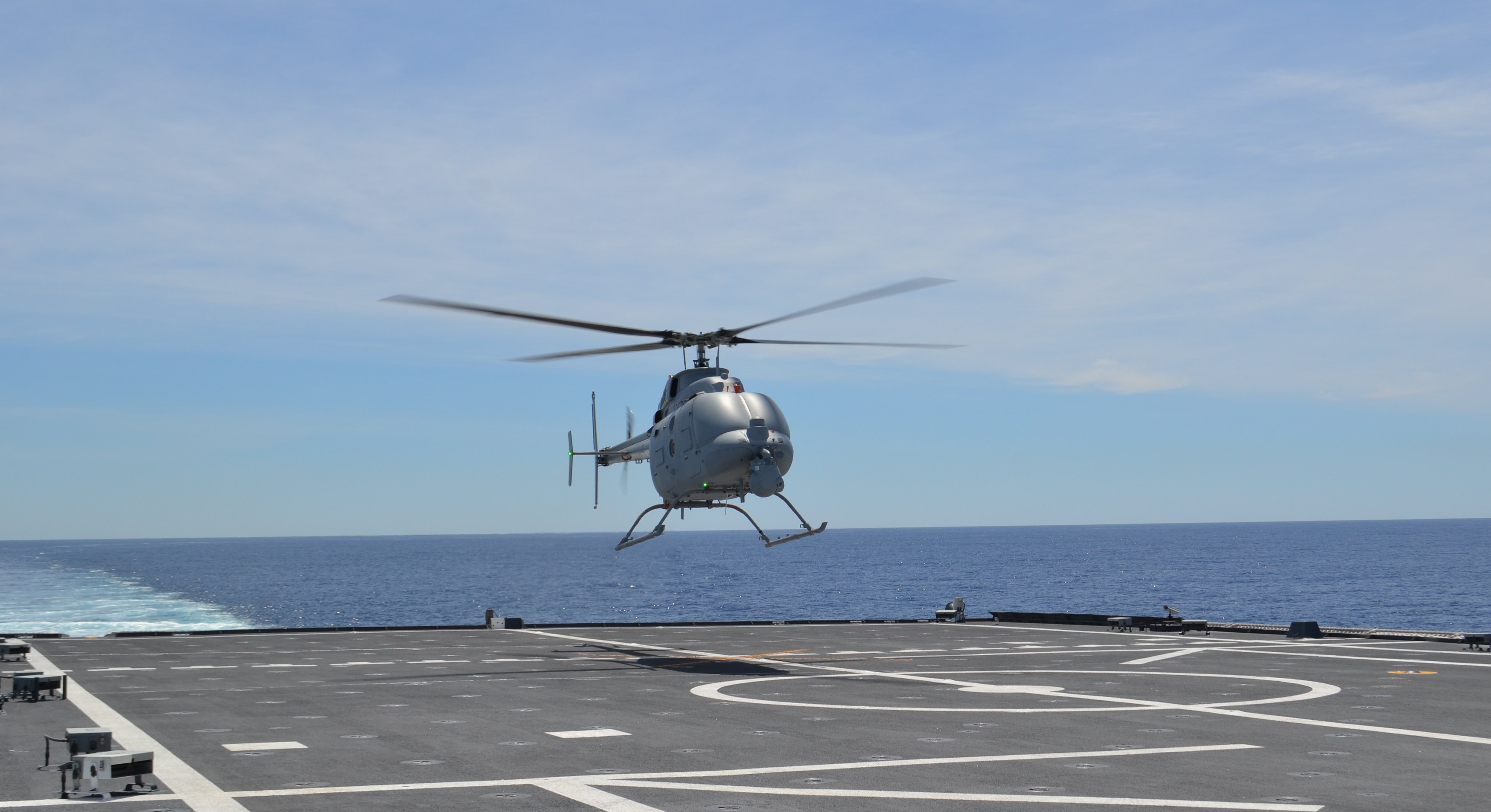

Fire Scout is a combat proven, autonomous helicopter system that provides real-time Intelligence, Surveillance, Reconnaissance, and Target-acquisition (ISR&T), laser designation and battle management to tactical users without relying on manned aircraft or space-based assets. Fire Scout has the ability to operate from any air-capable ship or land base in support persistent ISR&T requirements.
The MQ-8C Fire Scout is the Navy's next generation autonomous helicopter. The MQ-8C Fire Scout's airframe is based on the commercial Bell 407, a mature helicopter with more than 1,600 airframes produced and over 4.4 million flight hours. Combined with the maturity of Northrop Grumman's autonomous systems architecture, Fire Scout meets customer requirements for ship-based and land-based autonomous systems. It also has the ability to autonomously take-off and land on any aviation-capable ship and from prepared and unprepared landing zones. This enhancement significantly increases range and endurance (more than double) and payload capacity (more than triple). The MQ-8C has completed developmental testing and is ready to deploy.
Northrop Grumman is a proven leader in Live, Virtual and Constructive (LVC) training solutions. Since 1999, Northrop Grumman has been providing worldwide LVC training for the U.S. Air Force (USAF). Affordable, resilient and secure, our systems use open architecture and modular scenarios to adapt to any challenge the future may hold.
Whereas other companies claim LVC capability, Northrop Grumman is the only one with demonstrated successes in connecting the live environment to actual warfighter simulators. Also, as more and more countries add various aircraft to their fleets, they will need the interoperable, on-demand, global LVC training solution offered by Northrop Grumman.











